Research Study Spotlights
A new instructional technique can boost learning and is critical for socioemotional development. Do you know what it is or how to use it?
A recent paper published in the Journal of Applied School Psychology is one of the first to find evidence that coloring can be an effective classroom tool for anxious children. Here’s the latest
Researchers believe that play-based learning is critical to developing the fundamentals of lifelong learning. Play has been demonstrated to promote long-term learning (Zosh et al., 2017), increase connectivity in the brain, and fosters higher engagement with STEM in high school and college (LEGO Group, 2017). Experts in the science of play suggest these are the mechanisms that make play-based learning so effective.
In recent years, many early childhood educators have embraced the learning-through-play approach. This hands-on method of instruction is has been shown to increase children’s understanding and enjoyment of learning, however, a recent paper has demonstrated that hands-on activities are still not as effective as inquiry-based activities.
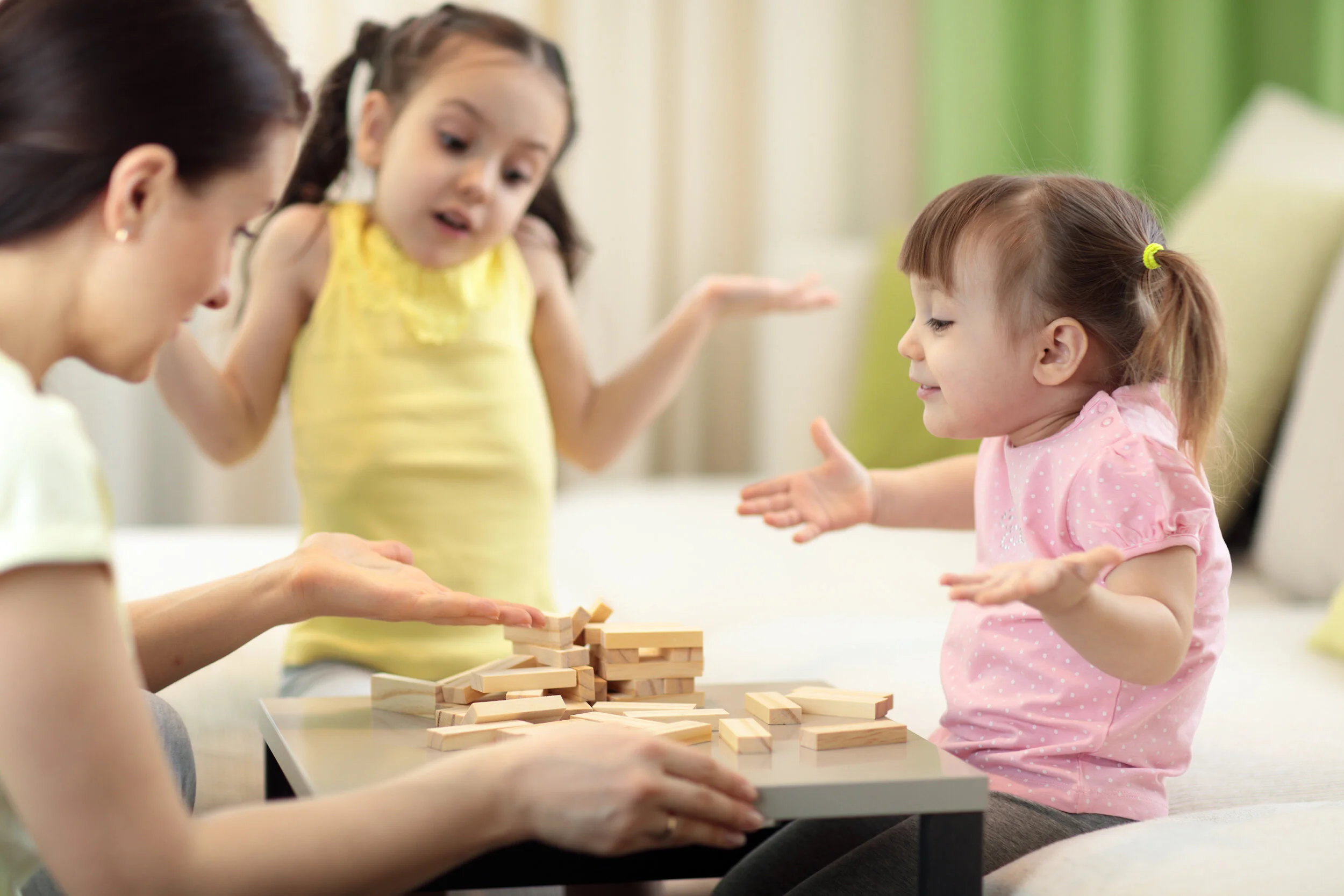
Social competencies are a critical component of early childhood education. Recent research has demonstrated that these core social competencies are predictive of classroom success and academic performance. To explore the potential benefits of mindfulness on learning, pro-social behavior, and self-regulation, developmental scientists from the Center for Investigating Healthy Minds implemented a 12-week mindfulness program in 6 pre-K classrooms in Madison, Wisconsin. Here are the results
Researchers at San Jose State University are investigating the link between natural curiosity and problem-solving abilities in preschoolers.
Developmental scientists have known for several decades that the kitchen provides a perfect laboratory for young learners. This article enumerates the skills children have the opportunity to learn while cooking, including gross and fine motor, executive function, and science skills!
Gratitude is an important prosocial emotion. In addition to facilitating and strengthening interpersonal bonds, gratitude has also been known to increase happiness, life satisfaction, and overall well-being. This paper investigates whether gratitude actually translates into pro-social behaviors.
Inquiry-based learning has been known to bolster learning in science for several decades, however, scant research has examined the effect of inquiry-based learning on children’s and teacher’s enjoyment of and motivation to do science. This paper explores the effects of inquiry-based engineering activities on science engagement, excitement, and comprehension.
Kitchen science falls under the umbrella of experiential science. This category of informal learning capitalizes on the invisible science processes embedded in daily life. Cooking is a particularly important type of experiential science because it is a fairly universal practice, transcending countries, cultures, and economic status, allowing for broad accessibility that is rare in science opportunities generally.
Halloween hijinks, in the form of stealing candy, was studied by social psychologist, Edward Diener, and colleagues in 1967. They conducted a study of 1,300 children’s trick or treating behavior in Seattle, Washington to understand the psychological mechanisms of candy theft.
Number literacy is an important competency in all walks of life. Children’s familiarity and competence with numbers entering formal education is predictive of long-term academic success, including performance on the SATs. This paper explores best-practices in early childhood math education.
Childhood fear can be tough to combat, especially when the fear is difficult to face like the monster under the bed. Almost two-thirds of preschool-age children suffer from the occasional nocturnal fear, however, almost 15% suffer from severe and sometimes debilitating anxiety at night. This paper explores the role of fantasy-thinking in nocturnal fears.
Dramatic play is a type of imaginative, pretend play where children act out the role of a character. Dramatic play has been implicated in the development of theory of mind abilities in children and adults, as it allows individuals to embody the perspective and mindset of another. This study investigates whether dramatic play can foster the development of socioemotional skills in preschool-age children.
Sleep is of critical importance for health and well-being. Insufficient amounts of sleep have been linked to poor cognitive and self-regulatory competencies, increased risk of heart disease and illness, and can even impact mental wellness. A 2020 study found regular bedtimes and sleep habits are particularly critical for toddlers. Here’s the science behind sleep.
Scientists have been studying self-control, or the ability to delay gratification for over 50 years. That’s because early measures of self-control are predictive of future success in academic achievement, healthy living, and even wealth. This study examines how kids of 2020 performed to previous generations
Planning a trip to the beach? The seashore is an excellent opportunity to engage your child in novel science experiences. National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC) recently published an article listing the top 10 STEM activities to introduce your child to science through play! Here are the top 3.
On August 5, 2020, People and Nature published a study from the University of Boulder, Colorado. This study provided a comprehensive overview of the literature surrounding the impact of nature on children’s well-being.
Math can be a daunting subject for many kids and families, but it doesn’t have to be. The National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC) in collaboration with the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) suggests that making children more comfortable with math can begin as a toddler. Increasing you and your child’s familiarity and comfort with numbers can start with basic math concepts. Here are some ways to incorporate math-talk in your daily life!
Healthy eating is a challenge facing America. With rising rates of heart disease, diabetes, and childhood obesity, healthy eating habits is an important area of research for parents and scientists. Unfortunately, preschool-age children can be neophobic, especially with food. This means they are unwilling to taste or try foods they don’t know. Often times, this also tends to be healthy foods like fruits and veggies. Here’s how to battle neophobia with your child.
Developmental scientists conducted a study to investigate whether a STEM storybook could promote science learning and science talk in children ages 4-5 years old. Here are the results.
Children who were encouraged to think and dress like their characters were better at keeping calm and continuing to try the challenging task then peers who were not dressed up as fictional characters. This “Batman Effect” was particularly strong for the youngest kids.
Proactivity is key to lifelong success. From educational obtainment to career advancement, cultivating a child who seeks opportunities to learn and grow is an important task for all parents. According to the Character Lab, a group of scientists dedicated to learning how to promote positive traits in children, the development of proactivity can be influenced following these tips.
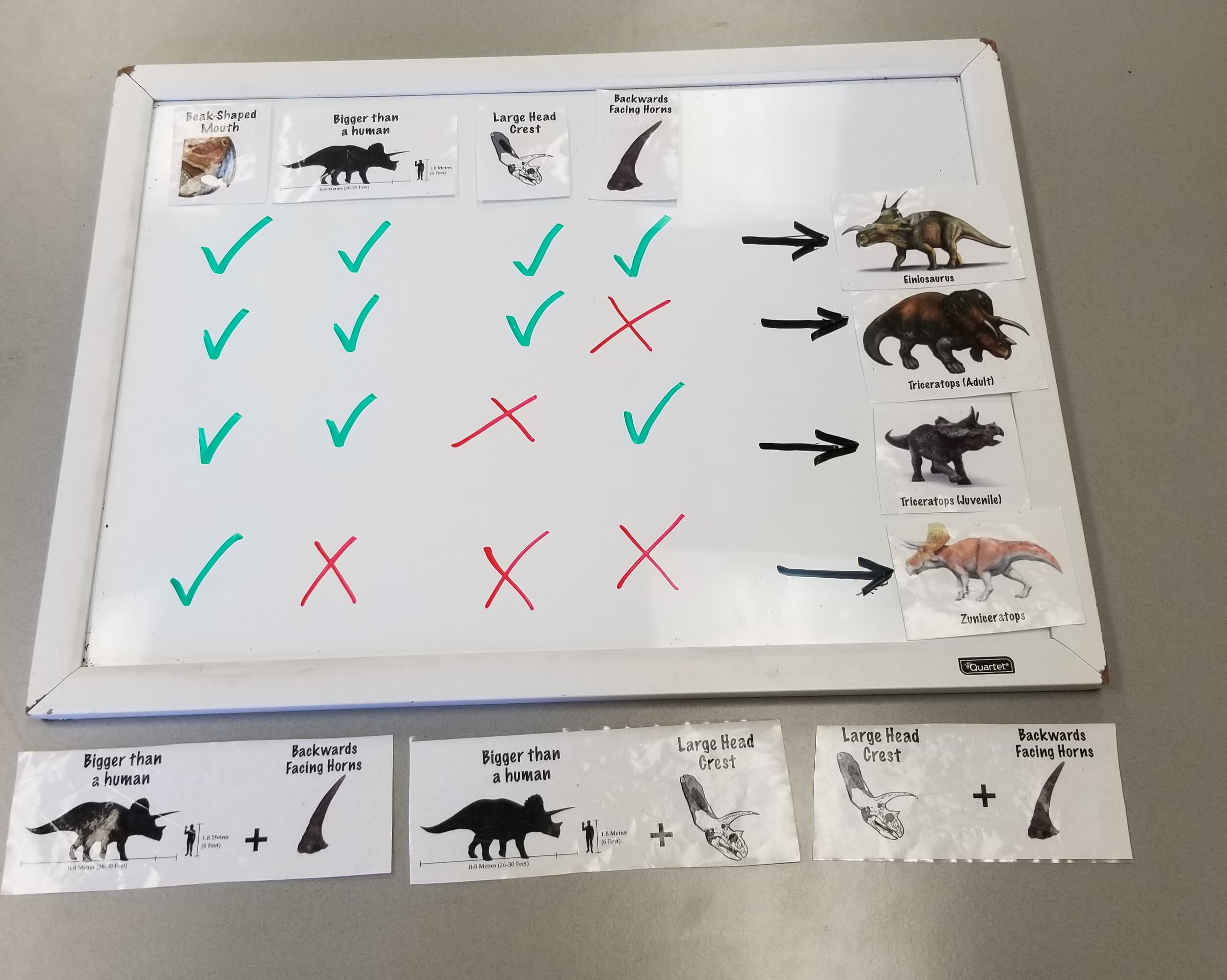
STEM Identity means your child is able to “think about themselves as a science learner and develop an identity as someone who knows about, uses and sometimes contributes to science,” (CAISE, 2018). A growing body of research has identified early childhood as a critical time point for success in STEM fields (Mantzicopoulos, Patrick, & Samarapungavan, 2008; Morgan, Farkas, Hillemeier, & Maczuga, 2016). Here’s why:
Experimentation is the process of systematically investigating a topic. Developmental scientists have found that novel science skills begin to develop as early as 4 years old (Sobel, Yoachim, Gopnik, Meltzoff & Blumenthal, 2007). You can support the development of experimentation skills in your child to experiment with these easy tips!
Creativity and flexible thinking is a critical scientific tool. In a 2018 paper in the International Society of the Learning Sciences, the ability to think outside the box is linked to the ability to problem-solve effectively, construct new hypotheses, and explore real-world phenomena.
Tool affordance is when we utilize available items to fulfill a job they were not necessarily designed to do. For example, in the absence of a ruler, the thumb or shoe may offer a method of measurement. They have identified key features of an object that may suffice to accomplish their goal if they do not have access to the right tools. This skill is a key component of flexible thinking.